WIC Utility under Linux – Download link for Linux version.
You can use one of the download links below to download the Linux version of WIC Reset Utility. There are direct download links and links via Google Drive, the choice is yours.
Download wicreset.deb (Google Drive – Link update 27.11.2025)
Download Linux versions here (direct link)
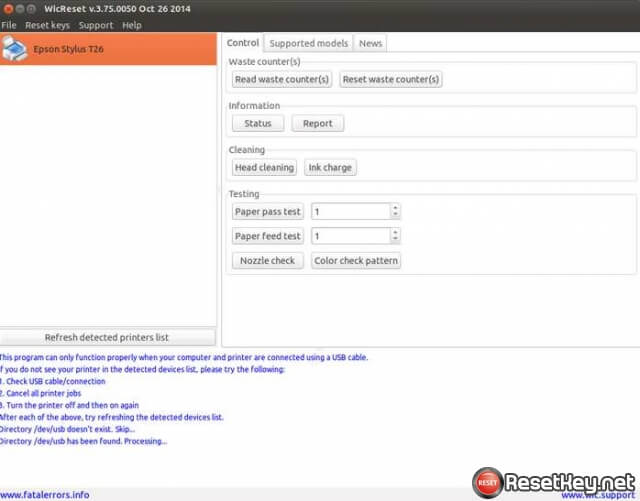
WicReset utility for Linux/Ubuntu Screenshots:
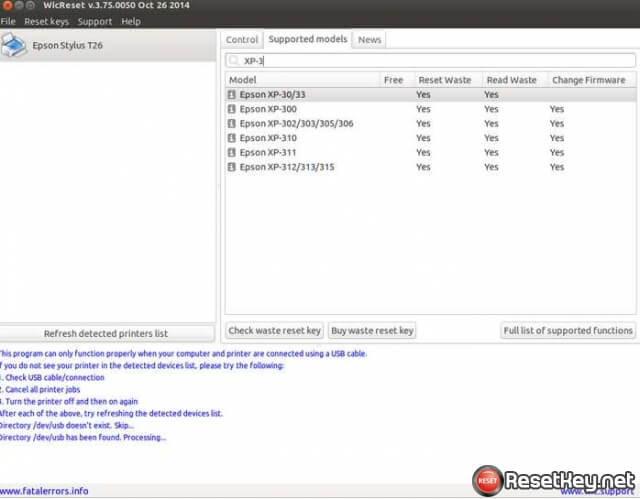
1. Differences between /dev/usb and /dev/bus/usb.
In the Linux system same devices may be presented on the different levels of the /dev directory, each of them using different drivers stack. For example inkjet printer can be accesed from the /dev/usb/lp0 and /dev/bus/usb/002/004, but in the first case it’s actually a printer (line printer 0) and in the second – generic usb device. WIC Reset will work only in the first case, thus creating aliases from /dev/bus/usb to /dev will not help to solve any problems and can be potentially harmful.
2. Access rights. Read me!
By default access rights for /dev/usb/lp* are defined like this:
ls l /dev/usb
crw-rw—- root lp 180, 0 Oct 27 02:38 lp0
Thus only root and members of `lp` group can access the printer.
There several ways to deal with this problem.
2.1. Add user to the `lp` group.
The simplest way is to add current user to the `lp` group and then reboot:
sudo usermod -a -G lp $(id -n -u)
sudo reboot
2.2. Change access rights for single printer.
Find our printer in /dev (for example, lp0) and then:
sudo chmod o+rw /dev/usb/lp0
2.3. Run application as root:
Warning!
Running application using root account may be dangerous.
You can use su, sudo or gksudo from gksu package.
su
wicreset
sudo wicreset
sudo apt-get install gksu
gksudo wicreset
When sudo is used system will not change user directory which may cause some warnings. On the other hand gksudo will always use root directory. In both cases all files created by the application will belong to the root, and therefore will be inaccessible by regular users. Also when application started using sudo or gksudo in KDE, GTK is unable to properly initialize all necessary resources.
2.4. Edit udev rules:
You can change default access rights for the printer using device manager.
For more details read udev manual page and this article: Writing Udev Rules by Daniel Drake.
3. Installation.
You can install WIC Reset either from console or using package manager.
3.1. Installation from console.
Install package using `dpkg` command from the directory, where package has been downloaded.
Fix missing dependencies using `apt-get`.
sudo dpkg i wicreset-i386.deb
sudo apt-get -f install
3.2. Installation from package manager.
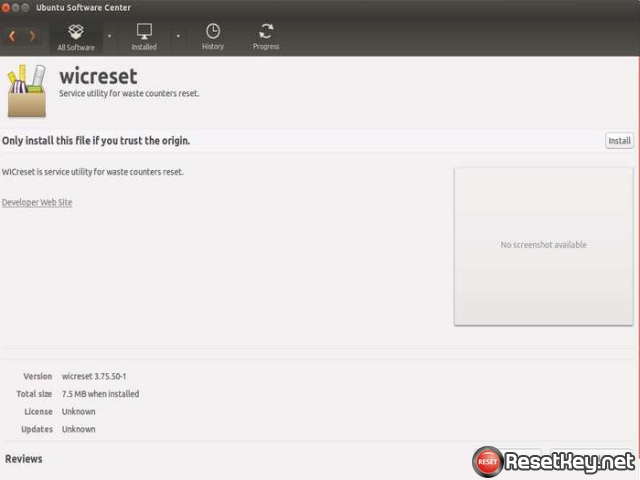
Supported distirbutions:
Ubuntu 13.00.4 Raring Ringtail.
Ubuntu 13.10.0 Saucy Salamander.
Ubuntu 14.00.4 Trusty Tahr.
Ubuntu 14.10.0 Utopic Unicorn.
Debian 8.0 Jessie.
Mint 15.0 Olivia.
Mint 16.0 Petra.
Mint 17.0 Qiana.
Derived distributions (Kubuntu, Xubuntu, Lubuntu, Edubuntu, etc.) should be supported as well.
Compiler Version:
GCC 4.7.3
Package Dependencies (dpkg-shlibdeps):
C/C++:
libc6 (>= 2.17)
libc6 (>= 2.3.6-6~)
libglib2.0-0 (>= 2.24.0)
libgcc1 (>= 1:4.1.1)
libstdc++6 (>= 4.6)
X11 & GTK+:
libx11-6
libsm6
libgtk2.0-0 (>= 2.24.0)
libgdk-pixbuf2.0-0 (>= 2.22.0)
Other:
libcairo2 (>= 1.6.0)
libpango1.0-0 (>= 1.18.0)
libpng12-0 (>= 1.2.13-4)
zlib1g (>= 1:1.1.4)
How to wicreset for Linux/Ubuntu manual:
Visit link at the begin of this post then click latest version to download wicreset for Linux/Ubuntu

Comments